LeetCode 001. Two Sum (Easy)
给定一个整数集合及一个目标数,从集合中找出两个数,使其和等于目标数。
原始问题
https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum/
Given an array of integers, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to a specific target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution.
1
2
3
4
5
| Example:
Given nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9,
Because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9,
return [0, 1].
|
解题思路
最直接的思路就是直接两次循环,判断两数之和是否等于目标数。这样做算法复杂度是O(n^2),效率很低。下面C语言版本的代码就是用这种方法实现的。
另一种高效的方法是使用字典HashMap,仅需一次循环即可,算法复杂度O(n)。以题目中的Example为例,算法原理可用下图说明:
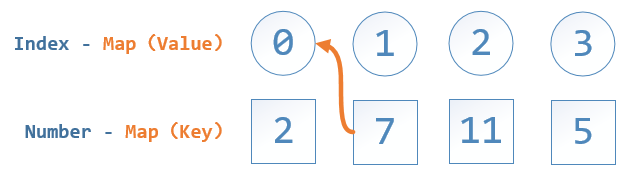
添加到Map中的元素是将数组中元素值Number作为Key,而对应的数组的索引值Index作为Value的。循环过程中,先判断此数字在Map中是否存在,若不存在的话,将其互补元素(即target - nums[i])添加到Map中,对应的值即为当前的i值;若存在的话,返回当前i值与Map[nums[i]]的值即可。具体实现见下面C++及Java版本的代码。
AC代码
C语言
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| int* twoSum(int* nums, int numsSize, int target) {
int i, j;
int * result;
result = (int *)malloc(2 * sizeof(int));
for (i = 0; i < numsSize - 1; i++) {
for (j = i + 1; j < numsSize; j++) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
result[0] = i;
result[1] = j;
return result;
}
}
}
return result;
}
|
C++
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
unordered_map<int, int> map;
vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (map.find(nums[i]) != map.end()) {
result.push_back(map[nums[i]]);
result.push_back(i);
return result;
}
map[target - nums[i]] = i;
}
return result;
}
};
|
Java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int [] result = new int[2];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (map.containsKey(nums[i])) {
result[0] = map.get(nums[i]);
result[1] = i;
return result;
}
map.put(target - nums[i], i);
}
return result;
}
}
|
相关题目
LeetCode 167. Two Sum II - Input array is sorted (Medium)
